Kanban: Continuous Improvement

To maintain a competitive advantage, businesses must seek to continuously improve and possibly reinvent their processes. Process Improvement is a proactive and systematic approach to streamlining business processes to improve the quality of outputs, lessen costs, and simplify the work.
Your business processes are not meant to be fixed. There will be inevitable changes to the way you do your work. These can be due to the presence of inefficiencies or defects, the advent of new technologies, changing market demands, new methodologies or ideas, and changing business needs and goals. To ensure your business process stays efficient, effective, and adequately satisfies your needs, reviewing and improving them proactively is essential.
Process improvement shouldn’t be thought of as a one-time project. To create sustainable change, organizations must have a continuous improvement mindset that is ingrained in their organizational culture.
This means that process improvement becomes a responsibility of ALL – not just the management or a selected few. Ideas and suggestions to better any business process can come from anyone within the organization. Having such a culture makes it easier for everyone to accept change and even become agents of change.
Benefits of Continuous Process Improvement
Nurturing a culture of continuous process improvement provides several benefits for organizations:
- Productivity – Process improvement initiatives commonly uncover manual and repetitive tasks that automation can make more efficient. Employees can then focus more on tasks that require their expertise.
- Employee Satisfaction – Efficient processes make employees more engaged as they can do work that capitalizes on their skills and knowledge instead of wasting time on tedious and manual tasks that can be handled by automation. Involving employees when forming and improving business processes will make them feel they have a voice and can affect organizational change.
- Quality and Consistency – Efficient processes will lessen the occurrence of defects and have ample quality checks to ensure standardized work. The introduction of automation will also reduce the risk of errors due to human intervention, which ultimately increases the quality of the business process.
- Customer Satisfaction – A well-oiled machine will only produce great results. High-quality products and services from your business process will satisfy customers because their needs are consistently met.
How Kanban Pushes for Process Improvement
As Kanban exposes inefficiencies and gaps within a business process, the team can see improvement opportunities. For example, when too much time is dedicated to a process step, the team can explore whether automation can speed things up. Even the introduction of WiP limits aims to improve the flow of work through a Kanban system and is thus a step towards process improvement.
But to ultimately take your Kanban practice further, it is through continuous process improvement models that these inefficiencies and gaps are to be addressed. When the team identifies the necessary improvement actions that need to take place, they will then update their Kanban system. The team then goes through their work using the new Kanban workflow, gathers data about their performance using the new process, and identifies opportunities to improve further.
The process improvement cycle then continues.
There are various process improvement methodologies that teams can explore to use alongside their Kanban practice that will help them measure and manage the flow of work through their Kanban system. To make the most of it, be sure to look into Kanban software solutions. They make it easier to gather process data and update your process steps when necessary.

Kaizen
Kaizen is a Japanese term that means “change for the better.” As a philosophy, the core of Kaizen is to instill a culture of continuous improvement in organizations and within individuals. It supports the idea that to create sustainable change, each employee in the organization must take part in executing process improvement initiatives.
As a business strategy, Kaizen requires the participation of all employees in Kaizen events. These are proactive initiatives that a company does to continuously improve different areas of the business through eliminating waste, standardization of work, and streamlining the process.
It is through the consistent execution of Kaizen events that organizations develop a process improvement mindset and culture. This makes it second nature to employees to continuously think of ways to produce better work.
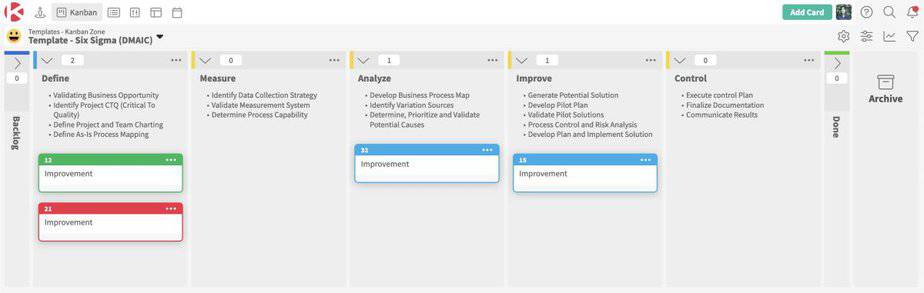
Six Sigma DMAIC
The Six Sigma DMAIC methodology is an approach for process improvement and problem-solving. It aims to eliminate waste in a business process while increasing the value given to the customer.
DMAIC is an acronym for the 5 phases of Lean Six Sigma:
- Define – Identifying the problem or customer need
- Measure – Gathering data to quantify the current process performance and the extent of the problem that needs to be solved
- Analyze – Examining what causes the problem
- Improve – Improving the current process by eliminating the root causes of the problem
- Control – Monitoring of process performance post-application of improvements and quantifying results of the change
Various Total Quality Management tools and techniques can be used in each phase of the DMAIC process to aid teams in their quest for continuous improvement. It should be noted that although the phases are presented linearly, process managers can find themselves iterating between phases to refine their findings and recommended solutions.
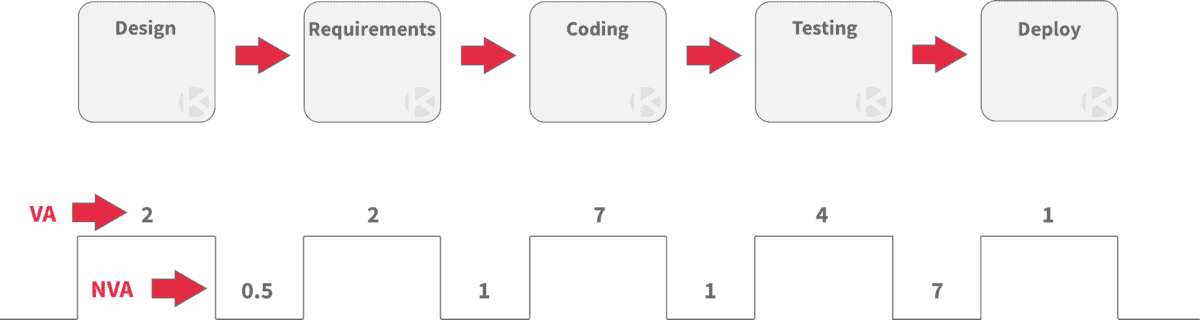
Value Stream Mapping
An understanding of the current process is essential to improve any business process. When teams visualize their work, they can better understand their process. This gives the team the necessary insight they need to effectively identify improvement areas and measure the extent of the improvement that comes out of their solutions.
Value Stream Mapping is a lean technique to document, analyze, and improve business processes. Creating a Value Stream Map gives teams a visual representation of the flow of materials and information required to produce a product or deliver a service.
The key in Value Stream Mapping is identifying which activities are value-adding and non-value-adding. The elimination of non-value-adding activities is designed to improve the quality of work, time to market, and overall customer value.
Bringing them all together
All three methodologies – Kaizen, Six Sigma DMAIC, and Value Stream Mapping – fall under the umbrella of Lean Thinking. With the right application and mindset, teams can explore using these models to frame their process improvement initiatives.
A continuous process improvement mindset is crucial for teams to be effective in their Kanban practice. You will discover that throughout the execution of your Kanban system, you will inevitably uncover inefficiencies, defects, or other issues in your current process. Whichever process improvement methodology you choose, you can be sure they complement Kanban effectively.